Cosmetic breast surgery
Cosmetic breast surgery interventions:
Breastplasty augmentation
Breast augmentation is a surgery usually performed on breasts of small volume, poorly developed, sometimes asymmetrical, poorly formed since puberty, but also on breasts that have decreased in volume after childbirth or simply for pure aesthetic purposes.
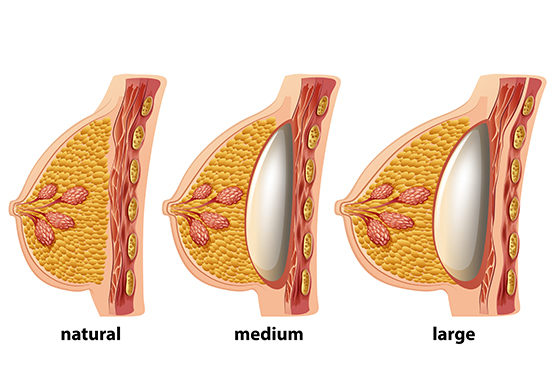
Which implant to choose?
The implants have experienced development and periods of success, particularly after the completion of complete safety studies (France and USA) that have demonstrated that these implants do not cause autoimmune disease.
However, the content as well as the quality of the implants have been modified so that they are more reliable than before.
Currently, saline-containing implants are being used less because of the risk of forming folds over time and, in some cases, deflating. Pre-filled implants of cohesive silicone gel are highly preferred, highly reliable and closer to the consistency of a breast.
There are usually two types of implants, those containing silicone and those filled with saline.
What scar to predict?
Three types are possible:
- The lower periareolar tract (at the junction between the colored skin of the areola and the white skin). This is the most used approach. It allows to put prostheses in front or back of the muscle but will not be possible if the diameter of the areola is too small and does not allow the passage of the prosthesis.
- The sub-mammary way. It carries a scar of 3 to 4 cm in the outer part of the under-mammary groove, usually of excellent quality. This is the most used approach route in the United States. It allows prostheses to be placed in front of or behind the muscle and offers a very nice exposure of the prosthesis reception area (better control of bleeding, position of prostheses …)
- The axillary way. It makes a scar in the armpit of 4 to 5 cm, vertical or horizontal. It is generally used to put prostheses behind the muscle and offers a less good exposure of the reception box of the prosthesis to the surgeon.
The position of the prosthesis
The implant can be placed in front of or behind the pectoralis major muscle. It depends on the shape and volume of the initial breast and the thorax. When the initial breast has sufficient volume, it is generally preferable to place the prosthesis in front of the muscle. Conversely, if the breast is very small and the patient is very thin, placing the prosthesis behind the muscle will hide it as much as possible. The retro-muscular prostheses are slightly more painful in the immediate aftermath (aches related to the detachment of the pectoralis major muscle). These pains are calmed by the usual analgesics and muscle relaxants.
Complications
In addition to the classic complications of any surgery (hematoma, cicatrization disorders …) infections and shells are the two specific complications of breast prostheses. They occur in less than 5% of cases and will be explained in detail by the center’s surgeon during the consultation.
Post opérative facts
Edema and bruising are common.
Wearing a non-armored sports bra is required for one month and sports are not allowed in the first month.
The radiological and ultrasound monitoring of the breast is not impeded by the prosthesis since it is behind the mammary gland.
Postoperative control is done on a regular basis, usually every year, and it is recognized that annual radiological control is preferable. The lifespan of the implants is variable but the current average is 10 years.
In addition to the cosmetic discomfort that it can sometimes cause, breast hypertrophy can also be responsible for discomfort in physical activity and back pain. This is why, in some cases of major hypertrophies, a surgical breast reduction can be supported by the social security and the mutuals.
The procedure consists into removing the excess mammary gland and skin, reposition and often reduce the size of the areola and remodel the remaining gland so as to go up. It is performed under general anesthesia and requires hospitalization for 24 to 72 hours.
Reassembling and reducing a hypertrophied breast requires the realization of inverted T scars: around the areola, vertical to the under-breast furrow and horizontal in the sub-mammary groove. Although every effort is made to ensure that scars are of the highest quality possible, the final result of these scars is unpredictable. Most often, they are flexible and of good quality.
During the 4 weeks following the breast reduction, the patient must wear a non-armored bra day and night.
Although it is sometimes possible, breastfeeding is not recommended after breast reduction because it promotes a new stretching of the breast and thus damage the aesthetic result. Finally, a decrease in the sensitivity of the nipple and breast skin is possible, but it is usually transient. The risks of complication of this surgery will be explained to you in consultation by the surgeon who will take care of you.
Breast lift, or mastopexy, consists in raising the breast. Indeed, with time and under the force of gravity, the skin and the gland of the breast tend to relax. This phenomenon can be accelerated by significant weight changes or pregnancy. This ptosis of the breast may or may not be associated with a diminution of its volume.
The objective of the ptosis treatment is to replace the nipple in a higher position, to reshape the glandular tissue, to remove the excess skin in the lower part of the breast and to redraw the remaining skin around the gland. If the breast is also empty, a breast prosthesis will be placed in front of or behind the muscle to fill it (cure of ptosis + breast prostheses).